
Agriculture is the backbone of Kenya’s economy, providing food, employment, and foreign exchange earnings. However, farmers in Kenya face many challenges such as limited access to markets, inadequate infrastructure, and climate change. Contract farming is one of the ways through which farmers in Kenya can increase their incomes, access markets and improve their livelihoods. In this article, we will look at what contract farming is, how it works in Kenya, the opportunities and challenges associated with it, and its profitability.
What is Contract Farming in Kenya?
Contract farming is a system of agriculture where farmers enter into a contractual agreement with buyers, processors, or exporters to produce a particular crop or livestock according to specified standards and quantities.
The contract specifies the quality, quantity, price, and delivery date of the produce. Contract farming is not new in Kenya, as it has been in existence since the 1960s. However, it has gained popularity in recent years due to its potential to increase farmers’ incomes and improve their livelihoods.
How Does Contract Farming Work in Kenya?
Contract farming in Kenya involves three main actors: the farmers, the buyers, and the intermediaries. The intermediaries are usually NGOs, government agencies, or private companies that facilitate the contract farming arrangements. The intermediaries provide technical support to the farmers, such as training on good agricultural practices, supply of inputs, and access to credit. They also link the farmers to the buyers and provide marketing support.
The buyers, on the other hand, provide the farmers with a guaranteed market for their produce and specify the quality and quantity required. The buyers could be processors, exporters, or retailers. They enter into long-term contracts with the farmers, which could last between one to five years. The buyers also provide technical support to the farmers, such as training on post-harvest handling, packaging, and transportation.
The farmers, on their part, agree to produce the required crop or livestock according to the specifications provided by the buyer. They also agree to sell their produce to the buyer at a specified price and within the agreed period. The farmers bear the production risks, such as pests, diseases, and adverse weather conditions.
Read this also: 10 Most Profitable Livestock Farming Business Ideas
What is the Concept of Contract Farming?
The concept of contract farming is based on the principle of mutual benefits. The farmers benefit from access to markets, technical support, and guaranteed prices for their produce.
The buyers benefit from a regular supply of quality produce, which they can process or export. The intermediaries benefit from the commissions they earn from facilitating the contract farming arrangements.
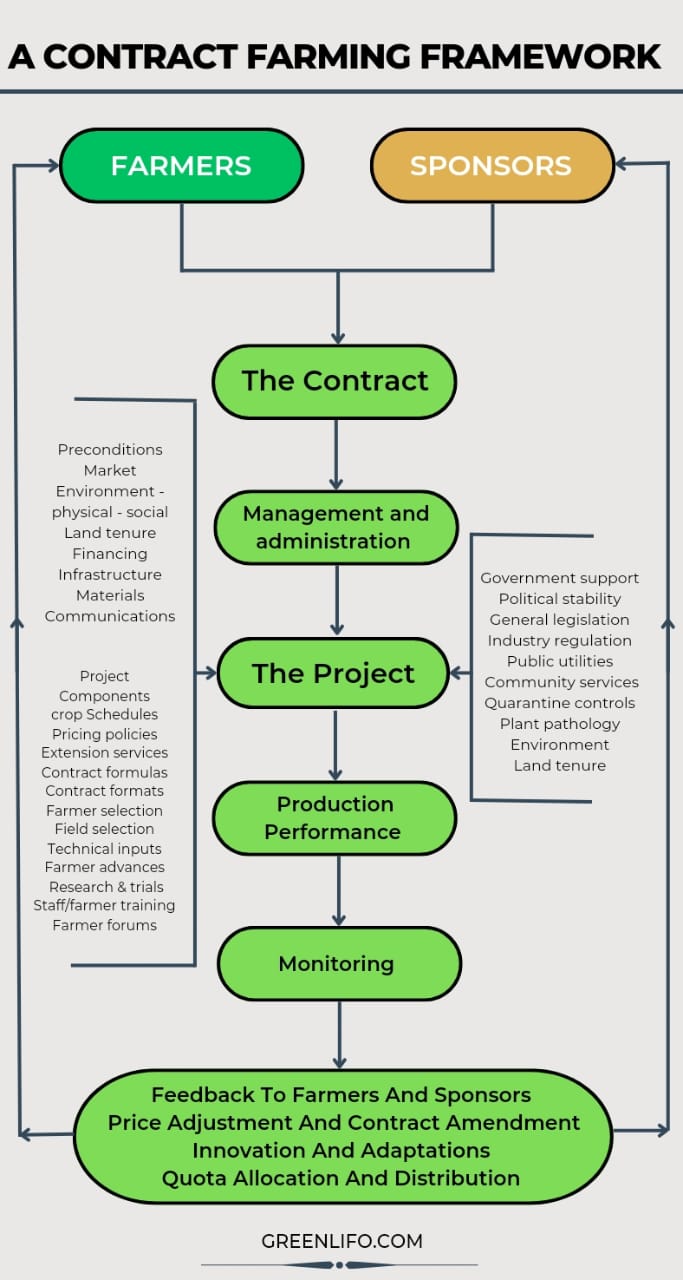
Contract Farming Opportunities in Kenya
Contract farming opportunities exist in various crops and livestock in Kenya, such as tea, coffee, horticulture, dairy, and poultry. The horticulture sector, particularly avocado farming, has seen significant growth in recent years due to contract farming.
According to the Kenya National Bureau of Statistics, Kenya’s avocado exports increased from 68,000 tonnes in 2016 to 84,000 tonnes in 2017. The demand for avocados in the international market, especially in Europe and China, has created opportunities for contract farming.
Other crops and livestock that present opportunities for contract farming in Kenya include maize, beans, sorghum, beef, and goat meat. Contract farming in maize and beans can help to improve food security in Kenya by increasing production and reducing post-harvest losses. Contract farming in livestock can help to improve the quality of meat and increase exports.
Is Contract Farming Profitable?
Contract farming can be profitable for farmers if the terms of the contract are favorable. The contract should specify a fair price for the produce, taking into account the cost of production, inputs, and the market price. The contract should also provide technical support to the farmers to ensure high yields and good quality produce. Additionally, the contract should provide for timely payment to the farmers.
The profitability of contract farming also depends on the crop or livestock being produced. For example, avocado farming in Kenya has been found to be profitable for smallholder farmers. A study conducted by the International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT) found that smallholder avocado farmers who participated in contract farming earned 35% more income than those who sold their produce in the open market.
However, contract farming can also be unprofitable for farmers if the terms of the contract are unfavorable. For example, if the price offered by the buyer is too low, the farmers may not be able to cover their production costs and make a profit. If the buyer fails to provide the required technical support, the farmers may not achieve high yields and produce low-quality produce.
What are the Problems Associated with Contract Farming in Kenya?
Despite the potential benefits of contract farming, there are also several challenges associated with it in Kenya. These include:
- Unequal bargaining power: Buyers and intermediaries may have more bargaining power than farmers, leading to unfavorable contract terms.
- Lack of transparency: Some buyers and intermediaries may not be transparent in their dealings with farmers, leading to mistrust and misunderstandings.
- Quality control: Some buyers may be strict in their quality requirements, making it difficult for smallholder farmers to meet the standards.
- Limited access to credit: Smallholder farmers may not have access to credit to finance their production activities, leading to low yields and poor quality produce.
- Limited access to inputs: Smallholder farmers may not have access to quality inputs, such as seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides, leading to low yields and poor quality produce.
- Dependence on a single buyer: Farmers who participate in contract farming may become dependent on a single buyer, making them vulnerable to market fluctuations and price fluctuations.
Is Contract Farming Good or Bad?
The question of whether contract farming is good or bad depends on the context in which it is practiced. Contract farming can be beneficial for farmers if the terms of the contract are favorable, and the buyers provide the required technical support and timely payment. Contract farming can also provide a guaranteed market for farmers, leading to increased incomes and improved livelihoods.
However, contract farming can also be detrimental to farmers if the terms of the contract are unfavorable, and the buyers do not provide the required technical support and timely payment. Contract farming can also lead to a concentration of power in the hands of buyers and intermediaries, leading to unequal bargaining power.
Therefore, it is important to ensure that contract farming arrangements are transparent, equitable, and beneficial to all parties involved. Government regulation and support can also help to address the challenges associated with contract farming in Kenya.
Does Contract Farming Improve Smallholder Income? The Case of Avocado Farmers in Kenya
Contract farming has been found to improve smallholder incomes in Kenya, particularly in the avocado sector. A study conducted by CIAT found that smallholder avocado farmers who participated in contract farming earned 35% more income than those who sold their produce in the open market. The study also found that contract farming led to increased yields and improved quality of produce.
Contract farming in the avocado sector in Kenya is facilitated by the Kenya Avocado Society (KAS), a farmer-based organization that links smallholder farmers to exporters. KAS provides technical support to the farmers, such as training on good agricultural practices and post-harvest handling. KAS also provides a guaranteed market for the farmers, leading to increased incomes and improved livelihoods.
In case you missed it: Best Feed For Dairy Goats: Ultimate Guide to Goat Nutrition
Advantages and Disadvantages of Contract Farming for Farmers
Advantages of Contract Farming for Farmers
- Guaranteed market for their produce
- Improved access to inputs, technical support, and credit
- Improved quality of produce
- Higher income for farmers
- Reduced risk of price fluctuations and market uncertainty
- Access to better markets and premium prices for high-quality produce
Disadvantages of Contract Farming for Farmers
- Unequal bargaining power, which can lead to unfavorable contract terms
- Dependence on a single buyer, which can make farmers vulnerable to market fluctuations and price fluctuations
- Limited control over the production process, which can lead to a loss of autonomy for farmers
- Limited access to alternative markets, which can restrict farmers’ choices and limit their ability to negotiate better terms.
Conclusion
Contract farming is an important agricultural marketing system in Kenya, which can provide a guaranteed market for smallholder farmers, leading to increased incomes and improved livelihoods. However, contract farming can also be associated with several challenges, such as unequal bargaining power, lack of transparency, and limited access to inputs and credit.
To ensure that contract farming arrangements are transparent, equitable, and beneficial to all parties involved, government regulation and support are necessary. Contract farming in Kenya should be practiced in a manner that promotes the interests of both farmers and buyers, with clear and fair contract terms, timely payments, and technical support.
In conclusion, contract farming can be a beneficial marketing system for smallholder farmers in Kenya, but it requires careful management and regulation to ensure that farmers receive fair prices for their produce and that their interests are protected.By addressing the challenges associated with contract farming and adopting a holistic approach to agricultural development, Kenya can unlock the potential of its smallholder farmers and promote sustainable agricultural growth and development.